Introduction to Bio LPG
Bio LPG (Biopropane or Bio Liquefied Petroleum Gas) is a renewable fuel produced from biomass, such as vegetable oils, animal fats and organic waste. This fuel is chemically identical to fossil LPG, meaning it can be used in the same applications, such as heating, cooking and transport, without the need to modify existing equipment.
Bio LPG Technical Description
From a technical point of view, Bio LPG is a biofuel composed mainly of propane and butane, similar to fossil LPG. It is obtained through biomass refining processes, mainly through the hydrogenation of oils and fats in processing units known as hydrotreaters. During this process, the triglyceride molecules of the biomass are broken down and reconfigured to form propane and butane, which are then liquefied to form Bio LPG.
Bio LPG is a sustainable alternative to traditional LPG because its production is carbon neutral. This is because the CO2 emitted during its combustion is offset by the CO2 that plants absorb during their growth, which contributes to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
In addition, Bio LPG has physical and chemical properties identical to fossil LPG, which means that it can be integrated into existing LPG infrastructure without the need for modifications. This makes it a practical and effective solution for decarbonization in residential, commercial and industrial applications.
CO2 Emissions from Bio LPG Production and Use
The production and use of Bio LPG generates significantly less CO2 emissions compared to conventional fossil fuels. During its production, CO2 emissions can vary depending on the efficiency of the process and the source of biomass used. However, in general, CO2 emissions in the production of Bio LPG are much lower than those of fossil LPG.
According to recent studies, CO2 emissions during the production of Bio LPG can be reduced by up to 80% compared to fossil LPG. This is because the biomass used to produce Bio LPG absorbs CO2 from the atmosphere during its growth, which balances out much of the emissions generated during production.
As for the use of Bio LPG in vehicles, CO2 emissions are also considerably lower compared to traditional fuels such as gasoline or diesel. Vehicles running on Bio LPG emit up to 50% less CO2 compared to those using fossil fuels. In addition, emissions of other pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter, are significantly lower, contributing to improved air quality.
In short, both the production and use of Bio LPG result in lower CO2 emissions, making it a much greener option than conventional fossil fuels. This feature is key to its adoption in sectors such as transport, where reducing emissions is a priority to meet international climate goals.
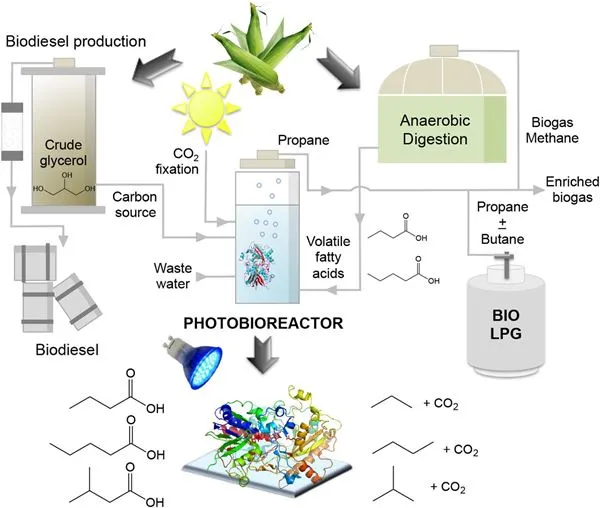
Origins and Evolution of Bio LPG
The concept of Bio LPG began to take shape in the 2000s, when the need for cleaner energy sources became more apparent. Early developments focused on converting vegetable oils and animal fats into biofuels. However, biopropane production did not take off until the 2010s, when oil and fat hydrogenation technology was perfected, allowing for the creation of liquid biofuels, including biopropane.
Throughout the 2010s, Bio LPG production experienced significant growth, driven by government policies promoting renewable energy. In Europe, the Renewable Energy Directive (RED II) played a crucial role, setting clear targets for the incorporation of biofuels into the energy mix.
Since 2020, Bio LPG production has continued to expand, with new projects in various parts of the world. The evolution of production technologies and the growing demand for sustainable fuels have made Bio LPG increasingly accessible and affordable.
Current Projects and Production Forecasts
The year 2024 marks a turning point in the Bio LPG industry. Global Bio LPG production is expected to exceed 3 million tonnes per year, thanks to the launch of new projects in Europe, North America and Asia. Among the most notable projects is the Neste plant in Rotterdam, which has become one of the largest producers of Bio LPG worldwide.
Another key project is TotalEnergies' project in La Mède, France, where the conversion of a traditional refinery into a biorefinery has enabled the production of large volumes of biopropane. In North America, companies such as Phillips 66 are leading the transition to Bio LPG with plants under development in California and Texas.
Forecasts for 2024 and beyond indicate that demand for Bio LPG will continue to increase, driven by the global energy transition and countries' commitments to reduce their carbon emissions. Production capacity is expected to continue to expand, with new projects planned in South America and Asia, regions where Bio LPG could play a crucial role in diversifying the energy matrix.
Key Locations and Main Operators
The main production areas of Bio LPG are currently concentrated in Europe, North America and Asia. Below are some of the most important locations:
- Rotterdam, Netherlands: Neste's Rotterdam plant is one of the largest producers of Bio LPG in the world, supplying several European countries.
- La Mède, France: TotalEnergies operates one of the leading biorefineries in Europe, with significant capacity for biopropane production.
- Texas, USA: Phillips 66 is developing key projects in Texas, with the aim of converting traditional refineries into Bio LPG production facilities.
- São Paulo, Brazil: In South America, Brazil is positioned as a potential hub for Bio LPG production, taking advantage of its vast agricultural and waste capacity.
Among the largest operators in the Bio LPG sector are: find:
- Neste: Based in Finland, Neste is a global leader in the production of renewable fuels, including Bio LPG. Its plant in Rotterdam is a benchmark in the industry.
- TotalEnergies: The French company has been a pioneer in the conversion of traditional refineries into biorefineries, with its project in La Mède as a prominent example.
- Phillips 66: This American company is investing heavily in the transition to renewable fuels, with several projects in development in the United States.
- Repsol: The Spanish multinational is exploring opportunities in the Bio LPG market, with projects in the planning phase in Spain and Portugal.
Bio LPG has established itself as a viable and sustainable option within the global energy landscape. From its inception to 2024, the industry has evolved significantly, with steady growth in production and project implementation worldwide. With continued technological innovation and government support, Bio LPG is likely to play a key role in the transition to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
References
- https://www.neste.com
- https://www.totalenergies.com
- https://www.phillips66.com
- https://www.repsol.com
- https://www.iea.org/reports/bioenergy
- https://www.glpautogas.info/documentos/what-is-bio-lpg.pdf